Cats savor sunlight. Their bodies radiate warmth, and most of them greatly dislike cold weather. Similar to our reptilian friends, felines tolerate temperatures around 60ºF to 70ºF but really thrive in the 86ºF to 100ºF zone. Even so, it isn’t unusual for your cat’s ears to sometimes feel cold because their outer and more exposed body parts, such as ears and paws, lose warmth first. Occasionally, though, severely cold ears may be a warning sign of hypothermia or frostbite, along with other unusual conditions. Here’s how to tell if you should take your cat to the vet or simply crank up the thermostat.

Why Are Cats’ Ears Cold?
A cat having cold ears can be totally normal. Their ears, tail, and paws are more exposed to the environment than other parts of the body, and the blood vessels in their ears are more susceptible to the ever-changing outside conditions than in body parts that are more centralized and protected by the body. The ears also lose heat faster because of this and are used for thermoregulation. Other areas of your cat that may feel colder are the tip of their tail and their paws. So, it could just be a sign that your cat is cold. Your cat will generally curl up their body to preserve heat and warm themselves, so the ears should warm up too.
However, a cat’s ears should generally still feel warm to the touch, so ears that are very cold or that don’t warm up quickly while your cat is curled up could be a sign that something more serious is wrong. If your cat is an indoor/outdoor cat, they could have gotten too cold if they stayed outside in winter conditions, leading to frostbite or hypothermia, both of which can turn into an emergency situation very quickly.
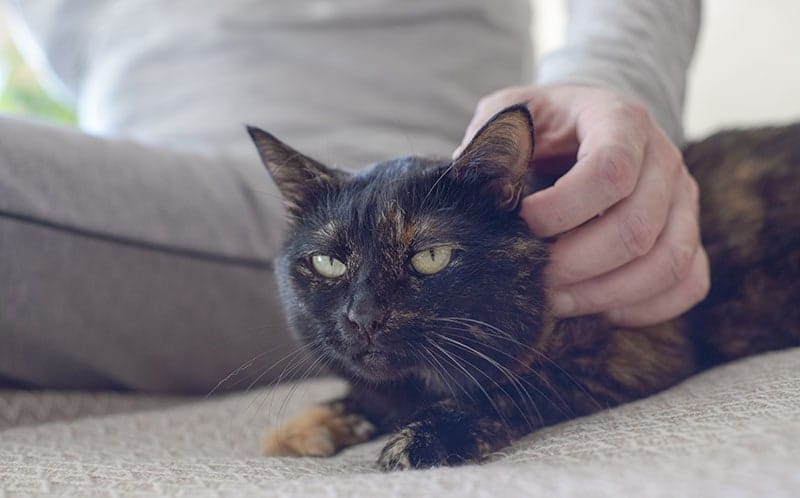

How to Tell If Your Cat Is Cold
Humans often wear layers of clothing, so to you, it might feel comfortable or even a little toasty in the room. Your cat may not agree, however, since they can’t pull on a sweater or squeeze into thermal underwear. Cats detest the cold. They may be trying to communicate their discomfort either through sending sour glares across the room from their favorite armchair or by snuggling extra close to you to garner extra warmth. Their ears and paws will often feel cold to the touch since they lose heat in those areas first.
Here are other key signs that your cat is too cold:
- Curling up
- Hiding their nose under their paws
- Snuggling close to you or other family members
- Sleeping in warm places, such as by the radiator or fireplace
- Searching for a blanket
- Hiding
- Shivering
You can comfort your cat by raising the thermostat, elevating their bed, and giving them plenty of blankets to snuggle in. Your cat may even make “biscuits” to show their gratitude.
How to Recognize Frostbite and Hypothermia
If you have an indoor cat, you’ll obviously want to keep them as comfortable as possible, but you probably won’t have to worry about any serious health complications that can come from the more severe temperatures outside.
Outdoor or indoor-outdoor cats require extra care to make sure they don’t get too cold. Temperatures lower than 45ºF can be particularly dangerous, especially in wet and stormy weather, if there is no adequate shelter or if the cat is not healthy or is a kitten or a senior cat.
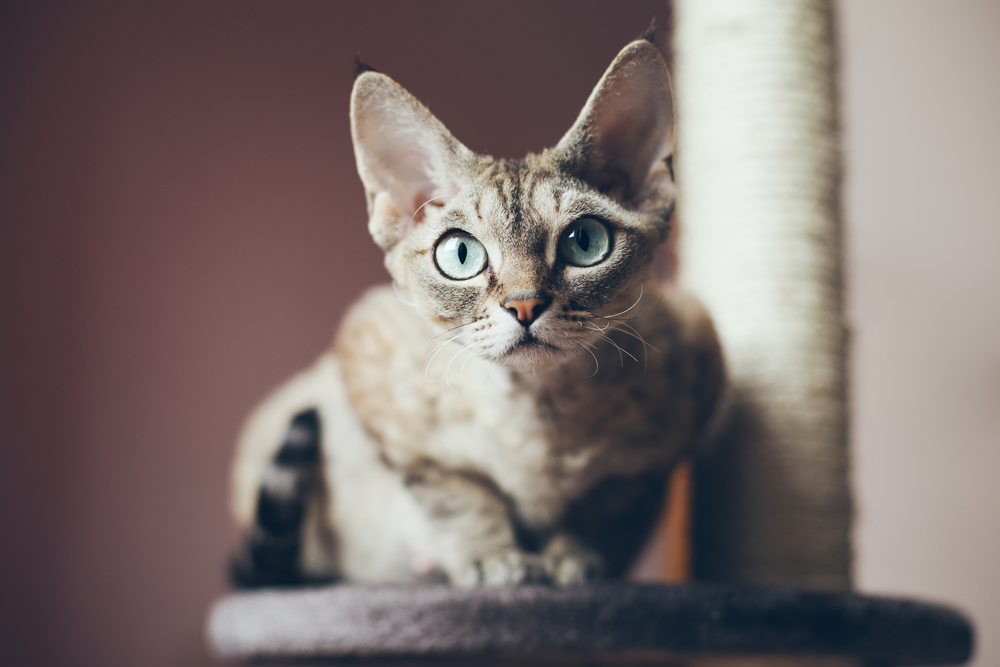

Frostbite
Freezing temperatures may lead to frostbite on their paws, ears, or tail and reduced body temperature or hypothermia.
Signs of frostbite include:
- Blisters or skin ulcers
- Pain, especially when you touch the affected areas that feel cold to touch
- Blue, gray, black, or purple discolored skin
- Swelling of the affected areas
- Blackened or dead skin in severe cases
Frostbite is a medical emergency that requires an immediate trip to the vet to try to recover the damaged tissue.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia can be equally scary. This condition happens when the body temperature drops too low. Cats have a normal body temperature range of 100ºF to 102ºF. If a feline’s temperature dips below 100ºF, they could be at risk of hypothermia, especially if they show these signs:
- Cold ears
- Pale gums
- Shivering
- Trouble breathing
- Weakness
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Unresponsiveness
- Loss of consciousness
- Collapse
- Coma
If you suspect hypothermia, bring your cat into a warm environment and wrap them in a blanket. Then get them to your veterinarian. The vet can accurately take your cat’s temperature, get their body temperature back up, and treat your cat as necessary.
It’s also important to note that shivering or shaking in cats can be a sign of low blood sugar or other health problems. If you’ve determined the problem is something besides the weather, you still need to take your cat to the vet for a checkup to make sure nothing is wrong. Hypothermic shock is a medical emergency.

Conclusion
Cold ears aren’t altogether uncommon in cats, since their ears and lower extremities lose warmth first. If you notice any signs of frostbite on their ears or signs of hypothermia and your cat has been outside in the cold or wet weather without shelter, warm them up and get them to your vet immediately. Red, swollen, discolored, blistered, painful, smelly, or hot ears are also concerning because that can be a sign of infection.
If you’re worried about your cat’s cold ears, take extra steps to make sure they’re warm. You might also want to take their temperature to ensure that their body is in the normal 100ºF to 102ºF range. If it’s more or less, contact your vet immediately, and let them know if you’ve noticed anything else unusual to help them diagnose the problem.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's an online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!
Featured Image Credit: effective stock photos, Shutterstock